lipid rich adrenal adenoma
For lipid-rich adenomas of the adrenal glands measuring under 4 cm in a patient with no underlying malignancy no follow up imaging is required 1. T2W diagnosis of adenoma may also be valuable in patients where chemical-shift MRI is limited due to motion artifact and in smaller nodules.

X Rays Ct Scans Mri And Other Tests For Adrenal Glands
The lipid-rich adrenal tumors were proved to be 16 non-hormone-secreting tumors 15 adenomas and one myelolipoma and 13 hormone-secreting tumors five subclinical cortisol-producing adenomas six aldosterone-producing adenomas and two adenomas that produced both cortisol and aldosterone.
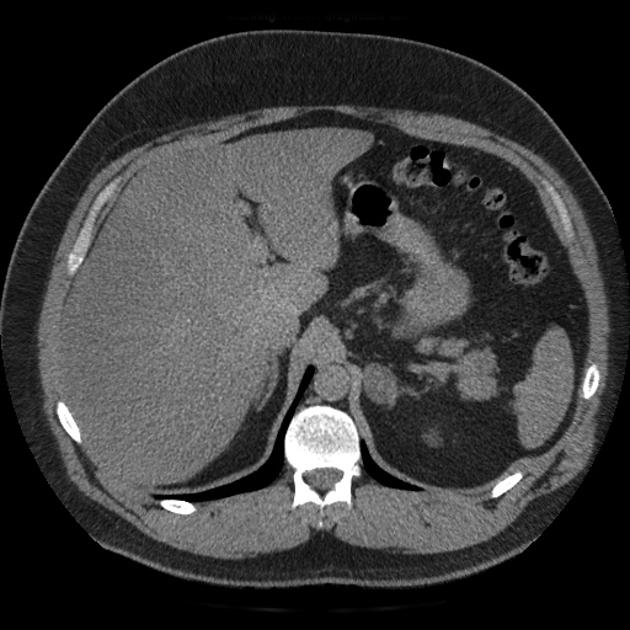
. And CB reviewed all radiological images. 70 of adenomas contain high intracellular fat and will be of low attenuation on unenhanced CT 45. Chemical shift magnetic resonance imaging CSI like unenhanced CT uses the lipid-rich property of most adenomas to differentiate benign from malignant. An adrenal gland adenoma is a tumor on your adrenal gland that isnt cancer but can still cause problems.
Essentially this is a measure of how dense or fat-containing the tumor is based on measurements of what is called Hounsfield Units HU. The same radiologists CM. Adrenal protocol CT was interpreted according to the following standard. In comparison to surrounding adrenal gland adenoma cells are larger with different cytoplasm increased variation in nuclear size Distinct cell borders cells have abundant foamy cytoplasm reminiscent of zona fasciculata Balloon cells.
Adrenal adenoma lipid rich or lipid poor Often homogeneous Increase in enhancement from arterial to venous phase Typically enhances 100 HU arterial 130 HU. Lipid-rich adrenal adenoma 3 cm 10 HU Rapid washout Signal loss Size usually stable Lipid-poor adrenal adenoma 3 cm 10 HU Rapid washout No. An adrenal lesion with Hounsfield units of less than 10 on unenhanced CT is a benign lipid-rich adrenal adenoma. The lower the Hounsfield Units lipid-rich.
Lipid-rich adenomas lose signal on the chemical-shift or out-of-phase opposed-phase images while lipid-poor lesions will not lose signal. Learn what causes them how to know if you might have one and how theyre treated. Each adrenal gland has two parts. Similar to unenhanced CT.
Thirty-five surgically resected adrenal adenomas were used. Its main utility is seen in evaluating dropout in out-of-phase versus in-phase images as well as in evaluating indeterminate heterogeneous density lesions suspected to have microscopic or macroscopic fat myelolipomas. Among remaining patients with unenhanced density 10 HU we selected. Adrenal lesions were characterized by placing an ROI over two-thirds of the surface area of the adenoma.
If this would be the case it would allow for a. The marked reduction in signal intensity between the in-phase and out of phase T1-weighted images indicates fatty content and therefore a lipid-rich adenoma. As in your case adrenal adenomas often are found incidentally on abdominal imaging. On MR lipid-rich adrenal adenomas may demonstrate out-of-phase signal dropout which again demonstrates that the lesion is a benign adenoma despite FDG avidity Fig.
In some cases functional adrenal adenomas can be treated with medications that block the function or lower the levels of the. If the initial unenhanced CT revealed adrenal nodule attenuation of less than 10 HU the nodule was considered a lipid-rich adenoma. The T2W properties of a lipid-rich adenoma may be useful when differentiating a lipid-rich adenoma from other adrenal masses which show microscopic fat on chemical-shift MRI including selected metastases ACC and rarely pheochromocytoma. Adrenal adenomas develop in the cortex.
To evaluate the relationship between lipid-rich cells of the adrenal adenoma and precontrast computed tomographic CT attenuation numbers in three clinical groupsMaterials and Methods. If the mass has an attenuation value of more than 10 Hounsfield units and therefore is lipid-poor it should be removed said Dr. The outer cortex and the inner medulla. Its not clear what causes adrenal adenomas to form.
Patients with unenhanced density of the adrenal mass 10 HU lipid-rich adenomas were excluded. Functional adrenal adenomas are typically treated with surgery. A density equal to or below 10 HU is considered diagnostic of a lipid-rich adenomas. Schteingart a professor of medicine and endocrinology at the University of Michigan Ann Arbor who has made particular study of incidentalomas.
None of the patients had pheochromocytoma or a malignant adrenal tumor. The absolute or relative percentage washout of contrast material on delayed contrast-enhanced CT is a highly specific test for the differentiation of lipid-poor and lipid-rich adrenal adenomas from adrenal nonadenomas. Thus if a lesion loses SI it is a lipid-rich adenoma Fig. Even though the relative percentage washout of the lipid-poor adenomas was lower than that of lipid-rich adenomas it was remarkably different from that of the nonadenomas.
Clusters of cells with enlarged lipid-rich cytoplasm seen in Cushing syndrome. Unenhanced attenuation of less than 10 HU was considered diagnostic of an adrenal adenoma. They tend to be more common in older adults and people who are obese as well as in those who have diabetes or high blood pressure. Using a safe threshold value of 10HU on a native CT scan results in a sensitivity of 70-79 and a high specificity of 96-98 for the diagnosis of an adenoma 5-7.
Removal of the affected adrenal gland usually resolves other medical conditions that may be present as a result of elevated adrenal hormones ie. Adrenal adenomas can be detected on non-contrast scans due to its low HU lipid-rich content signal drop out is seen in opp-phase. A lipid-rich mass is more likely to be a benign adenoma. If it does not lose SI all one can state is that the lesion does not contain lipid and is therefore not a lipid-rich adenoma.
Fatty are the more likely it is that the tumor is not a cancer but. Primary aldosteronism Cushings syndrome. Adrenal metastases should not have Hounsfield units of less than 10 on unenhanced CT. The present study was undertaken to evaluate the hypothesis that lipid-rich adrenal incidentalomas a hallmark of benign adrenal adenomas may not show excess growth andor develop excess hormonal secretion during short-term follow-up and that it might be possible to re-evaluate them after 5-year follow-up instead of at 1 to 2 years intervals.
The clinical diagnoses of the patients included 13 cases of primary aldosteronism 15 cases of Cushings syndrome and 7 non.

The Radiology Assistant Characterization Of Adrenal Lesions

The Radiology Assistant Characterization Of Adrenal Lesions

The Radiology Assistant Characterization Of Adrenal Lesions

Chemical Shift Mr And Precontrast Ct Scans Of Right Lipid Rich Adrenal Download Scientific Diagram


Posting Komentar untuk "lipid rich adrenal adenoma"